Isthmus

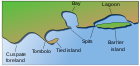
An isthmus (/ˈɪsməs, ˈɪsθməs/;[1] pl.: isthmuses or isthmi)[2] is a narrow piece of land connecting two larger areas across an expanse of water by which they are otherwise separated.[3] A tombolo is an isthmus that consists of a spit or bar, and a strait is the sea counterpart of an isthmus, a narrow stretch of sea between two landmasses that connects two larger bodies of water.
Isthmus vs land bridge vs peninsula
[edit]
Isthmus and land bridge are related terms, with isthmus having a broader meaning. A land bridge is an isthmus connecting Earth's major land masses. The term land bridge is usually used in biogeology to describe land connections that used to exist between continents at various times and were important for the migration of people and various species of animals and plants, e.g. Beringia and Doggerland.[4]
An isthmus is a land connection between two bigger landmasses, while a peninsula is rather a land protrusion that is connected to a bigger landmass on one side only and surrounded by water on all other sides. Technically, an isthmus can have canals running from coast to coast (e.g. the Panama Canal), and thus resemble two peninsulas; however, canals are artificial features distinguished from straits.[citation needed]
Major isthmuses
[edit]
The world's major isthmuses include:
- Karelian Isthmus in Europe
- Kra Isthmus in Mainland Southeast Asia
- Bird's Neck Isthmus in Western New Guinea
- Isthmus of Tehuantepec in Middle America
- Isthmus of Perekop in Ukraine
- Isthmus of Panama in Middle America
- Isthmus of Suez between North Africa and Western Asia
Of historic importance were:
The cities of Auckland, Madison, Manila, and Seattle are located on isthmuses.
Canals
[edit]Canals are often built across isthmuses, where they may be a particularly advantageous shortcut for marine transport. For example:
- The Panama Canal crosses the Isthmus of Panama, connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans
- The Suez Canal connects the Mediterranean Sea (part of the Atlantic Ocean) and the Red Sea (part of the Indian Ocean), cutting across the western side of the Isthmus of Suez, formed by the Sinai Peninsula
- The Crinan Canal crosses the isthmus between Loch Crinan and Loch Gilp, which connects the Kintyre peninsula with the rest of Scotland
- The Welland Canal in the Niagara Peninsula (technically an isthmus); it connects Lake Ontario to Lake Erie
See also
[edit]- Land bridge – Connection between two land form bodies
- List of isthmuses
- List of straits
Notes
[edit]- ^ "isthmus". CollinsDictionary.com. HarperCollins. Retrieved 2016-12-19.
- ^ from Ancient Greek ἰσθμός (isthmós) 'neck' LSJ entry ισθμός
- ^ "Isthmus". Britannica. Retrieved September 22, 2013.
- ^ "Land bridge | isthmus". Encyclopedia Britannica.